Selective Lazer Melting (SLM)
Selective Laser Melting or Metal Powder Bed Fusion is a 3D printing process which produces solid objects, using a thermal source to induce fusion between metal powder particles one layer at a time.
Most Powder Bed Fusion technologies employ mechanisms for adding powder as the object is being constructed, resulting in the final component being encased in the metal powder. The main variations in metal Powder Bed Fusion technologies come from the use of different energy sources; lasers or electron beams.
-
Types of 3D Printing Technology: Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS); Selective Laser Melting (SLM); Electron Beam Melting (EBM).
-
Materials: Metal Powder: Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Titanium.
-
Dimensional Accuracy: ±0.1 mm.
-
Common Applications: Functional metal parts (aerospace and automotive); Medical; Dental.
-
Strengths: Strongest, functional parts; Complex geometries.
-
Weaknesses: Small build sizes; Highest price point of all technologies.
Selective Lazer Melting (SLM)
Selective Laser Melting or Metal Powder Bed Fusion is a 3D printing process which produces solid objects, using a thermal source to induce fusion between metal powder particles one layer at a time.
Most Powder Bed Fusion technologies employ mechanisms for adding powder as the object is being constructed, resulting in the final component being encased in the metal powder. The main variations in metal Powder Bed Fusion technologies come from the use of different energy sources; lasers or electron beams.
-
Types of 3D Printing Technology: Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS); Selective Laser Melting (SLM); Electron Beam Melting (EBM).
-
Materials: Metal Powder: Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Titanium.
-
Dimensional Accuracy: ±0.1 mm.
-
Common Applications: Functional metal parts (aerospace and automotive); Medical; Dental.
-
Strengths: Strongest, functional parts; Complex geometries.
-
Weaknesses: Small build sizes; Highest price point of all technologies.
Selective Lazer Melting (SLM)
Selective Laser Melting or Metal Powder Bed Fusion is a 3D printing process which produces solid objects, using a thermal source to induce fusion between metal powder particles one layer at a time.
Most Powder Bed Fusion technologies employ mechanisms for adding powder as the object is being constructed, resulting in the final component being encased in the metal powder. The main variations in metal Powder Bed Fusion technologies come from the use of different energy sources; lasers or electron beams.
-
Types of 3D Printing Technology: Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS); Selective Laser Melting (SLM); Electron Beam Melting (EBM).
-
Materials: Metal Powder: Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Titanium.
-
Dimensional Accuracy: ±0.1 mm.
-
Common Applications: Functional metal parts (aerospace and automotive); Medical; Dental.
-
Strengths: Strongest, functional parts; Complex geometries.
-
Weaknesses: Small build sizes; Highest price point of all technologies.
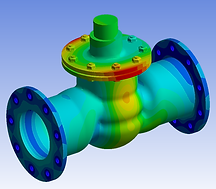
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS (FEA)
We at Forcyst have developed a method where once the concept is designed and approved, we prepare a problem statement and set the boundary conditions and carry out the Finite Element Analysis to validate the performance and failure modes of the designed product.
This method of analysis is used to verify the designed criterias to minimize the over-engineering at times. We carry out two types of FE Analysis, Static and Linear.
Static analysis basically involves zero internal effects, zero vibrations and zero impact whereas Linear Analysis involves, linear geometry, material and zero contact.
FEA is carried out through software including CFD that FORCYST team use in developing a product. FE analysis does add a cost to the project but it saves the time for unnecessarily over-designed or under designed prototyping.
The benefits of implementing FEA during the design process is that the product can be tested or analyzed with actual material properties. Thus this approach, helps to reduce and time and costing of project.
FORCYST also uses Finite Element Analysis as a method to carry out Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) studies.
If you would like to discuss your current or planned project then please connect with us at support@forcyst.com
Thus, Finite Element Analysis is a method where we can validate and prove our design calculations through engineering approach and methods.
Finite Element Analysis is broadly divided into following types;
-Stress
-Thermal
-Vibration
-Impact
-Crash
-Seismic